from Piers J. Sellers, the deputy director of Sciences and Exploration at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and acting director of its Earth Sciences Division. As an astronaut, he visited the International Space Station three times and walked in space six times.
I’M a climate scientist who has just been told I have Stage 4 pancreatic cancer.
This diagnosis puts me in an interesting position. I’ve spent much of my professional life thinking about the science of climate change, which is best viewed through a multidecadal lens. At some level I was sure that, even at my present age of 60, I would live to see the most critical part of the problem, and its possible solutions, play out in my lifetime. Now that my personal horizon has been steeply foreshortened, I was forced to decide how to spend my remaining time. Was continuing to think about climate change worth the bother?
After handling the immediate business associated with the medical news — informing family, friends, work; tidying up some finances; putting out stacks of unread New York Times Book Reviews to recycle; and throwing a large “Limited Edition” holiday party, complete with butlers, I had some time to sit at my kitchen table and draw up the bucket list.
Very quickly, I found out that I had no desire to jostle with wealthy tourists on Mount Everest, or fight for some yardage on a beautiful and exclusive beach, or all those other things one toys with on a boring January afternoon. Instead, I concluded that all I really wanted to do was spend more time with the people I know and love, and get back to my office as quickly as possible.
I work for NASA, managing a large group of expert scientists doing research on the whole Earth system (I should mention that the views in this article are my own, not NASA’s). This involves studies of climate and weather using space-based observations and powerful computer models. These models describe how the planet works, and what can happen as we pump carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The work is complex, exacting, highly relevant and fascinating.
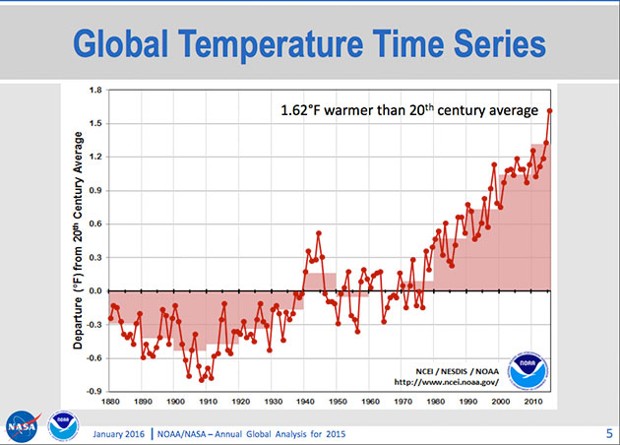
Last year was the warmest year on record, by far. I think that future generations will look back on 2015 as an important but not decisive year in the struggle to align politics and policy with science. This is an incredibly hard thing to do. On the science side, there has been a steady accumulation of evidence over the last 15 years that climate change is real and that its trajectory could lead us to a very uncomfortable, if not dangerous, place. On the policy side, the just-concluded climate conference in Paris set a goal of holding the increase in the global average temperature to 2 degrees Celsius, or 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit, above preindustrial levels.
While many have mocked this accord as being toothless and unenforceable, it is noteworthy that the policy makers settled on a number that is based on the best science available and is within the predictive capability of our computer models.
It’s doubtful that we’ll hold the line at 2 degrees Celsius, but we need to give it our best shot. With scenarios that exceed that target, we are talking about enormous changes in global precipitation and temperature patterns, huge impacts on water and food security, and significant sea level rise. As the predicted temperature rises, model uncertainty grows, increasing the likelihood of unforeseen, disastrous events.
All this as the world’s population is expected to crest at around 9.5 billion by 2050 from the current seven billion. Pope Francis and a think tank of retired military officers have drawn roughly the same conclusion from computer model predictions: The worst impacts will be felt by the world’s poorest, who are already under immense stress and have meager resources to help them adapt to the changes. They will see themselves as innocent victims of the developed world’s excesses. Looking back, the causes of the 1789 French Revolution are not a mystery to historians; looking forward, the pressure cooker for increased radicalism, of all flavors, and conflict could get hotter along with the global temperature.
Last year may also be seen in hindsight as the year of the Death of Denial. Globally speaking, most policy makers now trust the scientific evidence and predictions, even as they grapple with ways to respond to the problem. And most Americans — 70 percent, according to a recent Monmouth University poll — believe that the climate is changing. So perhaps now we can move on to the really hard part of this whole business.
The initial heavy lifting will have to be done by policy makers. I feel for them. It’s hard to take a tough stand on an important but long-term issue in the face of so many near-term problems, amid worries that reducing emissions will weaken our global economic position and fears that other countries may cheat on their emissions targets.
Where science can help is to keep track of changes in the Earth system — this is a research and monitoring job, led by NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and their counterparts elsewhere in the world — and use our increasingly powerful computer models to explore possible futures associated with proposed policies. The models will help us decide which approaches are practicable, trading off near-term impacts to the economy against longer-term impacts to the climate.
Ultimately, though, it will be up to the engineers and industrialists of the world to save us. They must come up with the new technologies and the means of implementing them. The technical and organizational challenges of solving the problems of clean energy generation, storage and distribution are enormous, and they must be solved within a few decades with minimum disruption to the global economy. This will likely entail a major switch to nuclear, solar and other renewable power, with an electrification of our transport system to the maximum extent possible. These engineers and industrialists are fully up to the job, given the right incentives and investments. You have only to look at what they achieved during World War II: American technology and production catapulted over what would have taken decades to do under ordinary conditions and presented us with a world in 1945 that was completely different from the late 1930s.
What should the rest of us do? Two things come to mind. First, we should brace for change. It is inevitable. It will appear in changes to the climate and to the way we generate and use energy. Second, we should be prepared to absorb these with appropriate sang-froid. Some will be difficult to deal with, like rising seas, but many others could be positive. New technologies have a way of bettering our lives in ways we cannot anticipate.
There is no convincing, demonstrated reason to believe that our evolving future will be worse than our present, assuming careful management of the challenges and risks. History is replete with examples of us humans getting out of tight spots. The winners tended to be realistic, pragmatic and flexible; the losers were often in denial of the threat.
As for me, I’ve no complaints. I’m very grateful for the experiences I’ve had on this planet. As an astronaut I spacewalked 220 miles above the Earth. Floating alongside the International Space Station, I watched hurricanes cartwheel across oceans, the Amazon snake its way to the sea through a brilliant green carpet of forest, and gigantic nighttime thunderstorms flash and flare for hundreds of miles along the Equator. From this God’s-eye-view, I saw how fragile and infinitely precious the Earth is. I’m hopeful for its future.
And so, I’m going to work tomorrow.
 Daniel1960, on 2016-January-09, 11:20, said:
Daniel1960, on 2016-January-09, 11:20, said:
 Help
Help